Research Areas
Yale engineering faculty are world leaders in research areas of critical importance to solving 21st century problems.
Research areas are primarily organized by department, though nearly every effort includes interdisciplinary collaborations.
Applied Physics
Optical Physics & DevicesThe Applied Physics optics research effort aims at understanding and controlling linear and nonlinear optical processes, and their interactions with modern nanostructured optical media and metamaterials. |
|
Physics of Novel MaterialsResearch on the fundamental physics and device aspects of novel materials is conducted by several Applied Physics faculty, in collaboration with faculty from other SEAS and Yale departments. |
|
Quantum Information & Device PhysicsDeveloping systems that employ quantum effects in order to process information, amplify signals, or detect electromagnetic radiation at or near the ultimate limits imposed by physical laws. |
|
Biomedical Engineering
Biomedical ImagingBiomedical imaging encompasses efforts in magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic resonance spectroscopy, nuclear medicine, optical light microscopy and image processing and analysis. |
|
Biomolecular EngineeringBiomolecular Engineering's express purpose is developing novel molecular tools, materials and approaches that are the focal point of applied and basic research within academia, industry and medicine. |
|
Drug DeliveryYale biomedical engineers work to develop alternate strategies for drug delivery, based on physical targeting, or placement of the delivery system at the target site, limiting its activity to that site. |
|
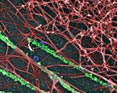
Tissue EngineeringWe are working to develop functional engineered tissues for vascular grafts and arteries, spinal cord repair, liver transplantation, and immune engineering. |
|
Chemical & Environmental Engineering
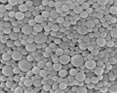
NanomaterialsNanomaterials research at Yale focuses on controlling material structure and spatial placement through the synthesis and assembly of new hard and soft materials. |
|
Interfacial PhenomenaThe boundary between two phases, the interface between the phases, has very different properties from that of the bulk phase and are important in a variety of chemical engineering processes. |
|
see more
Electrical & Computer Engineering
Computer EngineeringThe research focuses on reliable architectures and computing platforms that can sense and process physical data and generate semantical output events. |
|
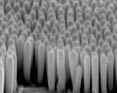
Electronic, Photonic & NanodevicesResearch focuses on the various physical phenomena that arise from novel material systems or novel device structures, with a goal toward possible applications in future generations of electronics and photonics. |
|
Mechanical Engineering & Materials Science
CombustionThe burning of a broad range of fuels will pose new challenges to the clean and efficient implementation of their combustion, which necessitates fundamental studies in well-defined and well-controlled environments. |
|
Robotics, Mechatronics, and Human Machine InterfaceWe conduct research in areas that synthesize the fields of robotics, machine design, human factors, and dynamic control. |
|