Undergraduate Curriculum Information
Yale’s Biomedical Engineering program offers the B.S. in Biomedical Engineering degree which prepares students for graduate studies in engineering and medicine, as well as careers in the Biomedical Engineering industry and other fields.
Examples of typical course sequences are presented below. Consultation with the program’s Director of Undergraduate Studies is expected to ensure the correct courses are taken by each enrolled student.
The Yale College requirements for the B.A. and B.S. degrees can be found here. The specific Biomedical Engineering degree requirements are detailed here.
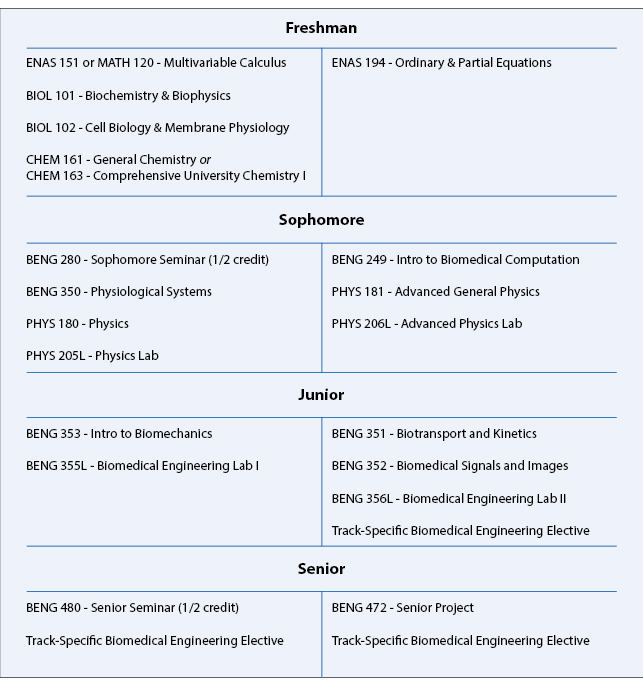
B.S. in Biomedical Engineering Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students with one year of Calculus
This program requires 11 technical term courses beyond the 10 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, ENAS 151 (or MATH 120), ENAS 194, PHYS 180, PHYS 181, PHYS 205, PHYS 206, CHEM 161 (or CHEM 163), and BIOL 101/102).
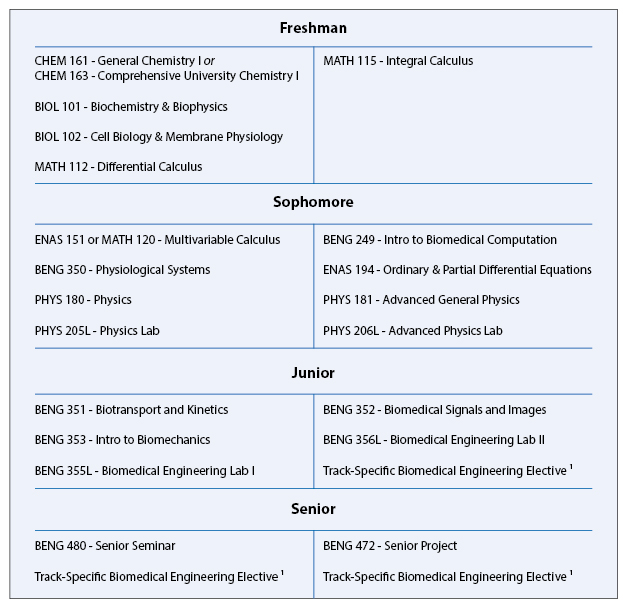
B.S. in Biomedical Engineering Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students who start with MATH 112
This program requires 11 technical term courses beyond the 10 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, ENAS 151 (or MATH 120), ENAS 194, PHYS 180, PHYS 181, PHYS 205, PHYS 206, CHEM 161 (or CHEM 163), and BIOL 101/102).
Combined B.S./M.S. in Biomedical Engineering
Exceptionally able and well-prepared students may complete a course of study leading to the simultaneous award of the Bachelor of Science and Master of Science degrees after eight terms of enrollment. See the Yale College Programs of Study for details. Below is a summary: