Three Electrical & Computer Engineering degree options are offered at Yale.
- ABET-accredited B.S. in Electrical Engineering: This degree program is appropriate for students interested in graduate study or a career in engineering. Also, graduates have found that this degree provides a solid foundation for careers in business, management consulting, banking, medicine, and law. Accredited by the Engineering Accreditation Commission of ABET, www.abet.org.
- B.S. in Engineering Sciences (Electrical): This degree program allows students to choose more courses from outside engineering, such as in economics, politics or another natural science. This degree prepares students for an engineering career or graduate study in engineering and establishes a strong technical background that is valued as a competitive asset in many other careers.
- B.A. in Engineering Sciences (Electrical): This degree program offers the most schedule flexibility while providing students with an engineering perspective on science and technology. This degree provides a significant benefit in the fields such as medicine, business, law, and public service.
In addition, a joint major in Electrical Engineering/Computer Science is available as described below.
Examples of typical course sequences are presented below. Consultation with the program’s Director of Undergraduate Studies is expected to ensure the correct courses are taken by each enrolled student.
The Yale College requirements for the B.A. and B.S. degrees can be found here. The specific Electrical Engineering degree requirements are detailed here.
ABET-accredited B.S. in Electrical Engineering Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students with one year of Calculus
This program requires 17 technical term courses beyond the 6 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, ENAS 130, ENAS 151 (or MATH 120), PHYS 180 and PHYS 181).
For students that enter Yale with the equivalent of one year of calculus in high school, a typical ABET-accredited B.S. in Electrical Engineering degree curriculum might include the following engineering specific courses in partial fulfillment of the thirty-six courses and distributional requirements of Yale College:
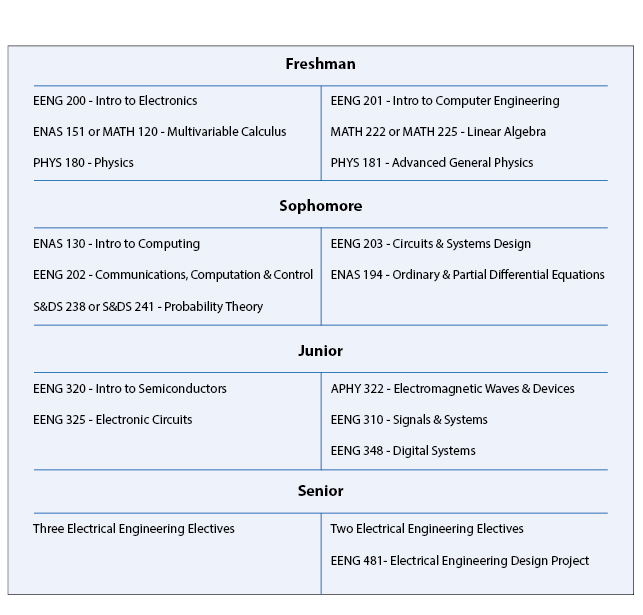
The Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering curriculum includes 4 elective courses, where three must be at the 400 level. Along with the appropriate EE courses the following Computer Science courses are also as engineering electives: 1) CPSC 365b: Design and Analysis of Algorithms; 2) CPSC 422b: Operating Systems; 3) CPSC 432b: Computer Music: Sound Representation and Synthesis; 4) CPSC 433b: Computer Networks; 5) CPSC 445a: Introduction to Data Mining; 6) CPSC 455a: Economics and Computation; 7) CPSC 463b: Machine Learning; 8) CPSC 470a: Artificial Intelligence; 9) CPSC 473b: Intelligent Robots; 10) CPSC 475a: Computational Vision and Biological Perception; 11) CPSC 478b: Computer Graphics
more info
ABET-accredited B.S. in Electrical Engineering Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students who start with MATH 112
This program requires 18 technical term courses beyond the 6 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, ENAS 130, ENAS 151 (or MATH 120), PHYS 180 and PHYS 181).
For students that start with MATH 112, a typical ABET-accredited B.S. in Electrical Engineering degree curriculum might include the following engineering specific courses in partial fulfillment of the thirty-six courses and distributional requirements of Yale College:
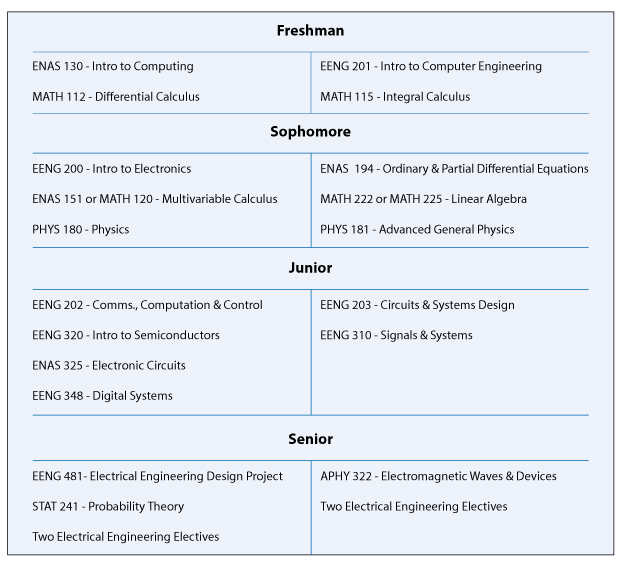
The Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering curriculum includes 4 elective courses, where three must be at the 400 level. Along with the appropriate EE courses the following Computer Science courses are also as engineering electives: 1) CPSC 365b: Design and Analysis of Algorithms; 2) CPSC 422b: Operating Systems; 3) CPSC 432b: Computer Music: Sound Representation and Synthesis; 4) CPSC 433b: Computer Networks; 5) CPSC 445a: Introduction to Data Mining; 6) CPSC 455a: Economics and Computation; 7) CPSC 463b: Machine Learning; 8) CPSC 470a: Artificial Intelligence; 9) CPSC 473b: Intelligent Robots; 10) CPSC 475a: Computational Vision and Biological Perception; 11) CPSC 478b: Computer Graphics
more info
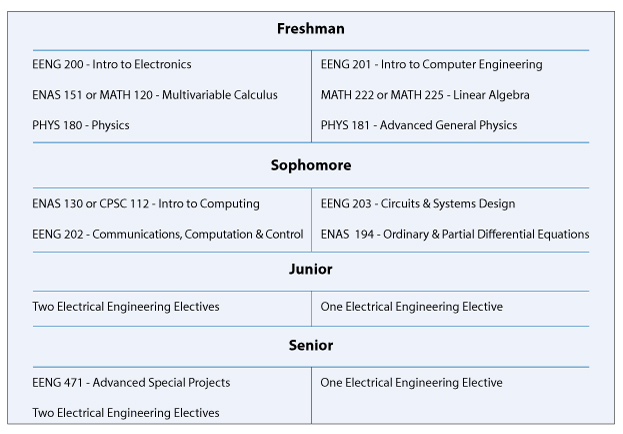
B.S. in Engineering Sciences (Electrical) Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students who start with one year of Calculus
This program requires 13 technical term courses beyond the 6 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, ENAS 130 (or CSC 112), ENAS 151 (or MATH 120), PHYS 180 and PHYS 181).
For students that start with the equivalent of one year of calculus in high school, a typical B.S. in Engineering Sciences (Electrical) degree curriculum might include the following engineering specific courses in partial fulfillment of the thirty-six courses and distributional requirements of Yale College:
more info
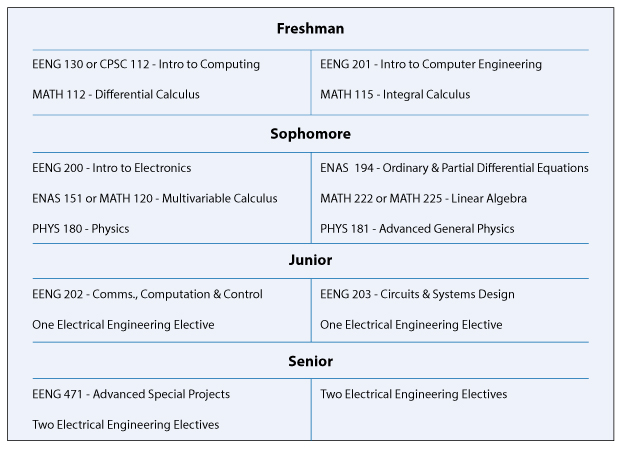
B.S. in Engineering Sciences (Electrical) Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students who start with MATH 112
This program requires 13 technical term courses beyond the 6 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, ENAS 130 (or CSC 112), ENAS 151 (or MATH 120), PHYS 180 and PHYS 181).
For students that start with MATH 112, a typical B.S. in Engineering Sciences (Electrical) degree curriculum might include the following engineering specific courses in partial fulfillment of the thirty-six courses and distributional requirements of Yale College:
more info
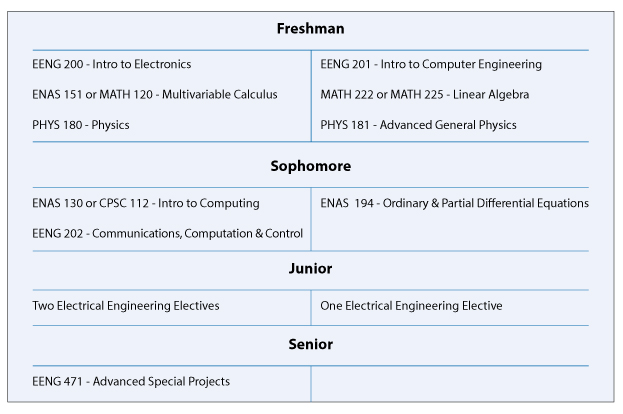
B.A. in Engineering Sciences (Electrical) Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students who start with one year of Calculus
This program requires 9 technical term courses beyond the 6 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, ENAS 130 (or CSC 112), ENAS 151 (or MATH 120), PHYS 180 and PHYS 181).
For students that start with the equivalent of one year of calculus in high school, a typical B.A. in Engineering Sciences (Electrical) degree curriculum might include the following engineering specific courses in partial fulfillment of the thirty-six courses and distributional requirements of Yale College:
more info
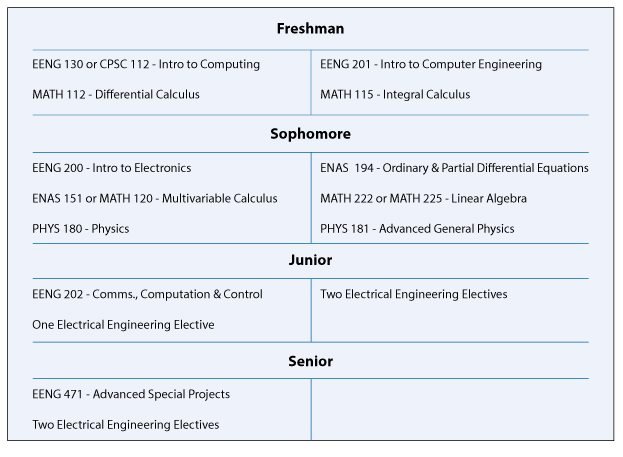
B.A. in Engineering Sciences (Electrical) Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students who start with MATH 112
This program requires 9 technical term courses beyond the 6 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, ENAS 130 (or CSC 112), ENAS 151 (or MATH 120), PHYS 180 and PHYS 181).
For students that start with MATH 112, a typical B.A. in Engineering Sciences (Electrical) degree curriculum might include the following engineering specific courses in partial fulfillment of the thirty-six courses and distributional requirements of Yale College:
more info
B.S. in Electrical Engineering/Computer Science
The joint major in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science is designed for students who want to integrate work in two fields. This major covers discrete and continuous mathematics, algorithm analysis and design, digital and analog circuits, sensor networks, signals and systems, systems programming, and computer engineering. The EENG/CPSC major provides a coherent core program and flexibility in the choice of technical electives.
Accreditation: Students wanting an ABET-accredited degree should consider the B.S. in Electrical Engineering.
Students should discuss their interests with both the DUS in Computer Science and the DUS in Electrical Engineering.
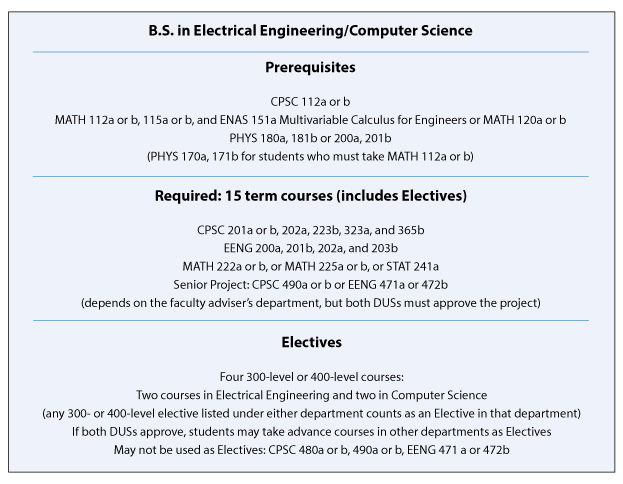
* Acceleration credits may be used to satisfy some of the prerequisites. However, since the B.S. programs in Electrical Engineering and in Engineering Sciences (Electrical) both limit the use of such credits, students who wish to retain the option of switching to these programs should consult the DUS in Electrical Engineering when planning their schedules.
A typical program in Electrical Engineering/Computer Science for students who have taken the equivalent of one year of calculus in high school (equal to MATH 112a or b and MATH 115a or b) and who have some programming experience (equal to CPSC 112a or b) would be:
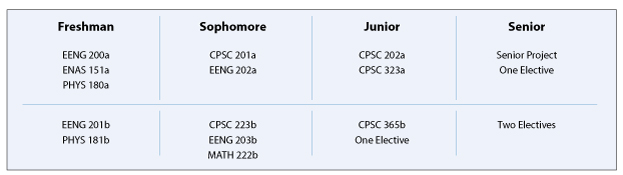
The entire Electrical Engineering/Computer Science major program must be approved by both the DUS in Electrical Engineering and the DUS in Computer Science.
more info









