Three Mechanical Engineering degree options are offered at Yale.
- ABET-accredited B.S. in Mechanical Engineering: This degree program is appropriate for students who plan on careers as practicing engineers in industry, consulting firms, and government. This program is also ideal for students who are considering a career in research or academia and plan to pursue graduate studies in Mechanical Engineering and related disciplines. Accredited by the Engineering Accreditation Commission of ABET, www.abet.org.
- B.S. in Engineering Sciences (Mechanical): This degree program is suitable for students who wish to gain significant expertise in Mechanical Engineering while combining this interest with related disciplines, such as materials science, architecture, and computer science, where the engineering experiences complement the other area of study. Students with this degree can also pursue graduate studies in mechanical engineering, applied physics, applied mathematics, materials science, and other related fields.
- B.A. in Engineering Sciences (Mechanical): This degree program is intended to provide a solid background in science and technology for students who may be pursuing careers in business, law, medicine, journalism, or politics.
Examples of typical course sequences are presented below. Consultation with the program’s Director of Undergraduate Studies is expected to ensure the correct courses are taken by each enrolled student.
The Yale College requirements for the B.A. and B.S. degrees can be found here. The specific Mechanical Engineering degree requirements are detailed here.
No courses may be taken Cr/D/F and count toward one of the Mechanical Engineering degree options.
ABET-accredited B.S. in Mechanical Engineering Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students with one year of Calculus
This program requires 20 technical term courses beyond the 8 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, ENAS 151 (or MATH 120), PHYS 180 (or PHYS 200), PHYS 181 (or PHYS 201), PHYS 165L (or PHYS 205L), PHYS 166L (or PHYS 206L), and CHEM 161 or higher (or AP score of 4 or 5).
For students who enter Yale with the equivalent of one year of calculus in high school, a typical ABET-accredited B.S. in Mechanical Engineering degree curriculum might include the following engineering specific courses in partial fulfillment of the thirty-six courses and distributional requirements of Yale College:
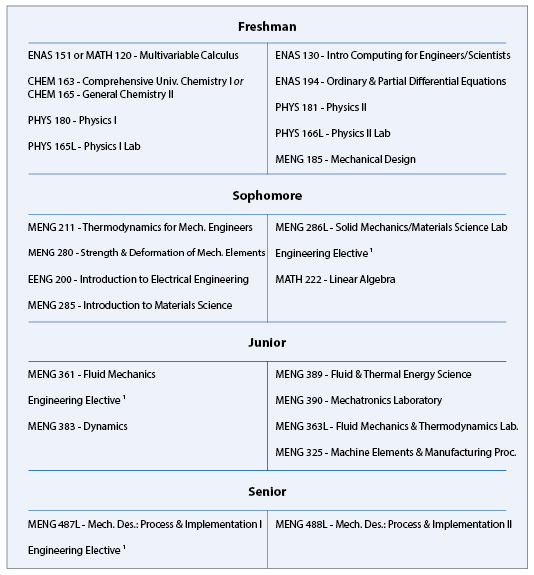
- Three approved technical electives chosen from the following: BENG 351 - Biotransport and Kinetics, BENG 353 - Introduction to Biomechanics, BENG 405 - Biotechnology and the Developing World, BENG 411 - Biomedical Microtechnology & Nanotechnology, BENG 421 - Fundamentals of Medical Imaging, BENG 434 - Biomaterials, BENG 435 - Biomaterials - Tissue Interactions, CENG 300 - Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, CENG 315 - Transport Phenomena, EENG 201 - Introduction to Computer Engineering, EENG 406 - Photovoltaic Energy, ENAS 400 - Making It, MENG 365 - Chemical Propulsion Systems, MENG 386 - Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 403 - Introduction to Nanomaterials & Nanotechnology, MENG 404 - Medical Device Design, MENG 386 - Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials, MENG 440 - Applied Numerical Methods for Algebraic Systems, Eigensystems, and Function Approximation, MENG 441 - Applied Numerical Methods for Differential Equations, MENG 459 - Neuromuscular Biomechanics, MENG 463 - Theoretical Fluid Dynamics, MENG 464 - Forces on the Nanoscale, MENG 469 - Aerodynamics, and other technical courses in consultation with the Director of Undergraduate Studies. One term course, either MENG 471, 472, 473, or 474 may be counted as one of the three technical electives.
These are the requirements for the B.S. in Mechanical Engineering for Yale College Class of 2021 and beyond. For the requirements for the Class of 2020, click here.
more info
ABET-accredited B.S. in Mechanical Engineering Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students who start with MATH 112
This program requires 20 courses (18.5 credits) beyond the 8 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, ENAS 151 (or MATH 120), PHYS 180 (or PHYS 200), PHYS 181 (or PHYS 201), PHYS 165L (or PHYS 205L), PHYS 166L (or PHYS 206L), and CHEM 161 or higher (or AP score of 4 or 5).
For students that start with MATH 112, a typical ABET-accredited B.S. in Mechanical Engineering degree curriculum might include the following engineering specific courses in partial fulfillment of the thirty-six courses and distributional requirements of Yale College:
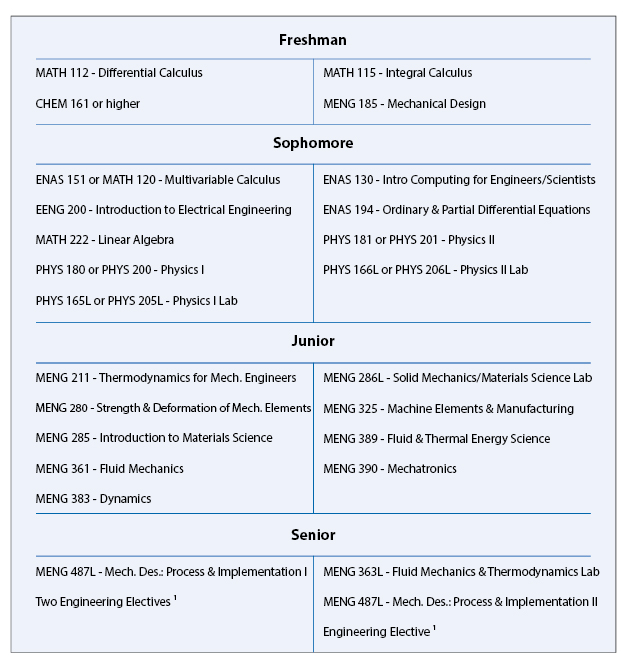
- Three approved technical electives chosen from the following: BENG 351 - Biotransport and Kinetics, BENG 353 - Introduction to Biomechanics, BENG 405 - Biotechnology and the Developing World, BENG 411 - Biomedical Microtechnology & Nanotechnology, BENG 421 - Fundamentals of Medical Imaging, BENG 434 - Biomaterials, BENG 435 - Biomaterials - Tissue Interactions, CENG 300 - Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, CENG 315 - Transport Phenomena, EENG 201 - Introduction to Computer Engineering, EENG 406 - Photovoltaic Energy, ENAS 400 - Making It, MENG 365 - Chemical Propulsion Systems, MENG 386 - Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 403 - Introduction to Nanomaterials & Nanotechnology, MENG 404 - Medical Device Design, MENG 386 - Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials, MENG 440 - Applied Numerical Methods for Algebraic Systems, Eigensystems, and Function Approximation, MENG 441 - Applied Numerical Methods for Differential Equations, MENG 459 - Neuromuscular Biomechanics, MENG 463 - Theoretical Fluid Dynamics, MENG 464 - Forces on the Nanoscale, MENG 469 - Aerodynamics, and other technical courses in consultation with the Director of Undergraduate Studies. One term course, either MENG 471, 472, 473, or 474 may be counted as one of the three technical electives.
These are the requirements for the B.S. in Mechanical Engineering for Yale College Class of 2021 and beyond. For the requirements for the Class of 2020, click here.
more info
B.S. in Engineering Sciences (Mechanical) Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students who start with one year of Calculus
This program requires 12 technical term courses beyond the 7 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, ENAS 151 (or MATH 120), PHYS 180 (or PHYS 200), PHYS 181 (or PHYS 201), PHYS 165L (or PHYS 205L), and PHYS 166L (or PHYS 206L).
For this degree, students typically take six core courses, MENG 280 - Mechanical Engineering I: Strength & Deformation, MENG 361 - Mechanical Engineering II: Fluid Mechanics, MENG 383 - Mechanical Engineering III: Dynamics, MENG 389 - Mechanical Engineering IV: Fluid and Thermal Energy Science, ENAS 194 - Ordinary & Partial Differential Equations, and MATH 222 - Linear Algebra with Applications, along with five additional technical courses in one or more of three tracks, plus a design-related or independent study course (1.0 course credits), such as MENG 404, 471, 472, 473, or 474, or MENG 487L and 488L. The three tracks are Solid Mechanics & Materials Science, Fluid Mechanics & Energy Conversion, and Mechanical Design.
For students that start with the equivalent of one year of calculus in high school, a typical curriculum for the B.S. degree in Engineering Sciences (Mechanical) might include the following engineering specific courses in partial fulfillment of the thirty-six courses and distributional requirements of Yale College:
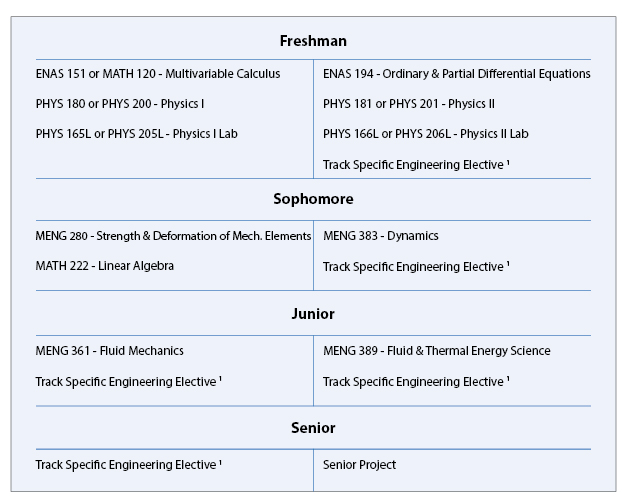
- Solid Mechanics & Materials Science Track: ENAS 130 - Introduction to Computing for Engineers/Scientists, EENG 200 - Introduction to Electrical Engineering, MENG 185 - Mechanical Design, MENG 211 - Thermodynamics for Mechanical Engineers, MENG 285 - Introduction to Materials Science, MENG 286L - Solid Mechanics/Materials Science Laboratory, MENG 386 - Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 403 - Introduction to Nanomaterials & Nanotechnology, BENG 353 - Introduction to Biomechanics, MENG 487L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation I, and MENG 488L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation II
Fluid Mechanics & Energy Conversion Track: ENAS 130 - Introduction to Computing for Engineers/Scientists, EENG 200 - Introduction to Electrical Engineering, CENG 315 - Transport Phenomena, MENG 185 - Mechanical Design, MENG 211 - Thermodynamics for Mechanical Engineers, MENG 363L - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics Laboratory, MENG 365 - Chemical Propulsion Systems, MENG 389 - Fluid & Thermal Energy Sciences, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 463 - Theoretical Fluid Dynamics, MENG 469 - Aerodynamics
Mechanical Design Track: EENG 200 - Introduction to Electrical Engineering, ENAS 118 - Engineering Innovation & Design or MENG 185 - Mechanical Design, ENAS 130 - Introduction to Computing for Engineers/Scientists, MENG 390 - Mechatronics Laboratory, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 404 - Medical Device Design, MENG 325 - Machine Elements and Manufacturing Processes, MENG 487L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation I, MENG 488L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation II
more info
B.S. in Engineering Sciences (Mechanical) Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students who start with MATH 112
This program requires 12 technical term courses beyond the 7 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, ENAS 151 (or MATH 120), PHYS 180 (or PHYS 200), PHYS 181 (or PHYS 201), PHYS 165L (or PHYS 205L), and PHYS 166L (or PHYS 206L).
For this degree, students typically take six core courses, MENG 280 Mechanical Engineering I: Strength & Deformation, MENG 361 Mechanical Engineering II: Fluid Mechanics, MENG 383 Mechanical Engineering III: Dynamics, MENG 389 Mechanical Engineering IV: Fluid and Thermal Energy Science, ENAS 194 Ordinary & Partial Differential Equations, and MATH 222 Linear Algebra with Applications, along with five additional technical courses in one or more of three tracks, plus a design-related or independent study course, such as MENG 404, 471, 472, 473, or 474 or 487L and 488L. The three tracks are Solid Mechanics & Materials Science, Fluid Mechanics & Energy Conversion, and Mechanical Design.
For students that start with MATH 112, a typical B.S. in Engineering Sciences (Mechanical) degree curriculum might include the following engineering specific courses in partial fulfillment of the thirty-six courses and distributional requirements of Yale College:
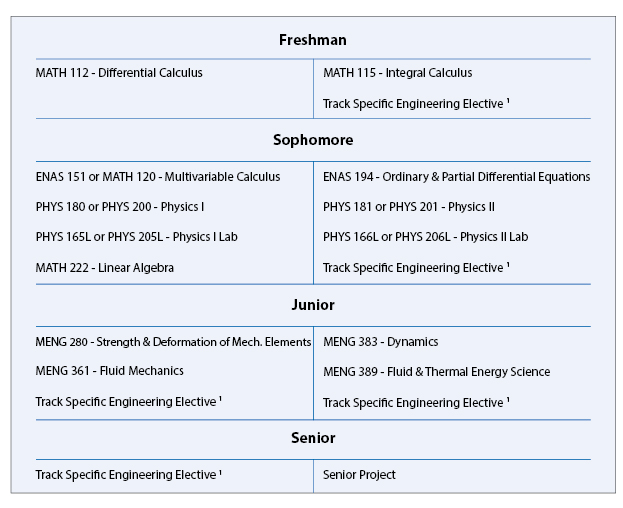
- Solid Mechanics & Materials Science Track: ENAS 130 - Introduction to Computing for Engineers/Scientists, EENG 200 - Introduction to Electrical Engineering, MENG 185 - Mechanical Design, MENG 211 - Thermodynamics for Mechanical Engineers, MENG 285 - Introduction to Materials Science, MENG 286L - Solid Mechanics/Materials Science Laboratory, MENG 386 - Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 403 - Introduction to Nanomaterials & Nanotechnology, BENG 353 - Introduction to Biomechanics, MENG 487L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation I, and MENG 488L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation II.
Fluid Mechanics & Energy Conversion Track: ENAS 130 - Introduction to Computing for Engineers/Scientists, EENG 200 - Introduction to Electrical Engineering, CENG 315 - Transport Phenomena, MENG 185 - Mechanical Design, MENG 211 - Thermodynamics for Mechanical Engineers, MENG 363L - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics Laboratory, MENG 365 - Chemical Propulsion Systems, MENG 389 - Fluid & Thermal Energy Sciences, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 463 - Theoretical Fluid Dynamics, MENG 469 - Aerodynamics
Mechanical Design Track: EENG 200 - Introduction to Electrical Engineering, ENAS 118 - Engineering Innovation & Design or MENG 185 - Mechanical Design, ENAS 130 - Introduction to Computing for Engineers/Scientists, MENG 390 - Mechatronics Laboratory, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 404 - Medical Device Design, MENG 325 - Machine Elements and Manufacturing Processes, MENG 487L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation I, and MENG 488L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation II
more info
B.A. in Engineering Sciences (Mechanical) Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students who start with one year of Calculus
This program requires 8 technical term courses beyond the 4 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, PHYS 170 (or PHYS 180) and PHYS 171 (or PHYS 181)).
For this degree, students typically take four core courses, MENG 280 - Mechanical Engineering I: Strength & Deformation, MENG 361 - Mechanical Engineering II: Fluid Mechanics, ENAS 194 - Ordinary & Partial Differential Equations, and MATH 222 - Linear Algebra with Applications, along with three additional technical electives in one of three tracks, plus a design-related or independent study course, such as MENG 404 or 471, 472, 473, or 474. The three tracks are Solid Mechanics & Materials Science, Fluid Mechanics & Energy Conversion, and Mechanical Design.
For students that start with the equivalent of one year of calculus in high school, a typical B.A. in Engineering Sciences (Mechanical) degree curriculum might include the following engineering specific courses in partial fulfillment of the thirty-six courses and distributional requirements of Yale College:
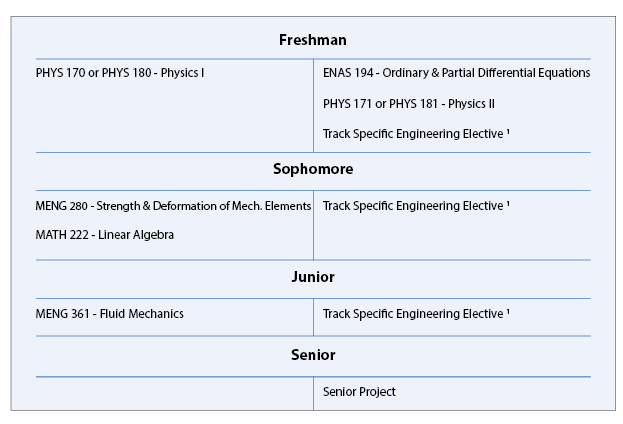
- Solid Mechanics & Materials Science Track: ENAS 130 - Introduction to Computing for Engineers/Scientists, EENG 200 - Introduction to Electrical Engineering, MENG 185 - Mechanical Design, MENG 211 - Thermodynamics for Mechanical Engineers, MENG 285 - Introduction to Materials Science, MENG 286L - Solid Mechanics/Materials Science Laboratory, MENG 386 - Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 403 - Introduction to Nanomaterials & Nanotechnology, BENG 353 - Introduction to Biomechanics, MENG 487L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation I, and MENG 488L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation II
Fluid Mechanics & Energy Conversion Track: ENAS 130 - Introduction to Computing for Engineers/Scientists, EENG 200 - Introduction to Electrical Engineering, CENG 315 - Transport Phenomena, MENG 185 - Mechanical Design, MENG 211 - Thermodynamics for Mechanical Engineers, MENG 363L - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics Laboratory, MENG 365 - Chemical Propulsion Systems, MENG 389 - Fluid & Thermal Energy Sciences, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 463 - Theoretical Fluid Dynamics, MENG 469 - Aerodynamics
Mechanical Design Track: EENG 200 - Introduction to Electrical Engineering, ENAS 118 - Engineering Innovation & Design or MENG 185 - Mechanical Design, ENAS 130 - Introduction to Computing for Engineers/Scientists, MENG 325 - Machine Elements and Manufacturing Processes, MENG 390 - Mechatronics Laboratory, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 404 - Medical Device Design, MENG 487L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation I, and MENG 488L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation II
more info
B.A. in Engineering Sciences (Mechanical) Typical Course Sequence
Course Sequence for students who start with MATH 112
This program requires 8 technical term courses beyond the 4 prerequisite courses (MATH 112, MATH 115, PHYS 170 (or PHYS 180) and PHYS 171 (or PHYS 181)).
For this degree, students typically take four core courses, MENG 280 - Mechanical Engineering I: Strength & Deformation, MENG 361 - Mechanical Engineering II: Fluid Mechanics, ENAS 194 - Ordinary & Partial Differential Equations, and MATH 222 - Linear Algebra with Applications, along with three additional technical electives in one of three tracks, plus a design-related or independent study course, such as MENG 404 or 471, 472, 473, or 474. The three tracks are Solid Mechanics & Materials Science, Fluid Mechanics & Energy Conversion, and Mechanical Design.
For students that start with MATH 112, a typical B.A. in Engineering Sciences (Mechanical) degree curriculum might include the following engineering specific courses in partial fulfillment of the thirty-six courses and distributional requirements of Yale College:

- Solid Mechanics & Materials Science Track: ENAS 130 - Introduction to Computing for Engineers/Scientists, EENG 200 - Introduction to Electrical Engineering, MENG 185 - Mechanical Design, MENG 211 - Thermodynamics for Mechanical Engineers, MENG 285 - Introduction to Materials Science, MENG 286L - Solid Mechanics/Materials Science Laboratory, MENG 386 - Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 403 - Introduction to Nanomaterials & Nanotechnology, BENG 353 - Introduction to Biomechanics, MENG 487L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation I, and MENG 488L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation II
Fluid Mechanics & Energy Conversion Track: ENAS 130 - Introduction to Computing for Engineers/Scientists, EENG 200 - Introduction to Electrical Engineering, CENG 315 - Transport Phenomena, MENG 185 - Mechanical Design, MENG 211 - Thermodynamics for Mechanical Engineers, MENG 363L - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics Laboratory, MENG 365 - Chemical Propulsion Systems, MENG 389 - Fluid & Thermal Energy Sciences, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 463 - Theoretical Fluid Dynamics, MENG 469 - Aerodynamics
Mechanical Design Track: EENG 200 - Introduction to Electrical Engineering, ENAS 118 - Engineering Innovation & Design or MENG 185 - Mechanical Design, ENAS 130 - Introduction to Computing for Engineers/Scientists, MENG 390 - Mechatronics Laboratory, MENG 400 - Computer-Aided Engineering, MENG 404 - Medical Device Design, MENG 325 - Machine Elements and Manufacturing Processes, MENG 487L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation I, and MENG 488L - Mechanical Design: Process and Implementation II
more info







